Thermodynamics diagram vapor liquid chapter saturated Diagram pressure constant line lines solved including Liquid closed container volume boil if diagram water phase temperature pressure thermodynamics constant steam supercritical left will description exchange compressed
homework and exercises - Thermodynamics compression work - Physics
A rigid tank of volume v_1=0.15 m^3 initially contains water at t_1=50 Pv diagrams thermodynamics thermo waals Diagram water study answer
Water initially problem piston cylinder kpa contained device has solved stops fitted transcribed text been show
Solved problem 3.44 water initially at 200 kpa and 300°c isExample: using a t-v diagram to evaluate phases and states Diagram phases states examplePhase diagrams.
Solved on this t-v diagram, is the pressure constant only onTv diagram for water Homework and exercisesDiagram phase.

Thermodynamics diagram gas ideal water region equation critical point represented shaded indicates zone
Subcooled vaporization ch3Thermodynamics lecture Thermodynamics lecture 3Diagram tv pure substance thermodynamics pressure points.
Diagram water volume specific compression thermodynamics work constant kg case curve secondPhase diagram water temperature pressure chemistry graph liquid gas solid diagrams constant point critical vapor labeled celsius read axis degrees Water t-v diagram this homework is due before theTv diagram of pure substance in thermodynamics.


Chapter 3 | Thermodynamics

Water T-v Diagram This homework is due before the | Chegg.com

Temperature - Volume (T-v) diagram for Phase Change Process - YouTube

Example: Using a T-v diagram to evaluate phases and states - YouTube

Tv Diagram For Water - Wiring Diagram

Solved Problem 3.44 Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is | Chegg.com

Solved on this T-V diagram, is the pressure constant only on | Chegg.com

A rigid tank of volume V_1=0.15 m^3 initially contains water at T_1=50
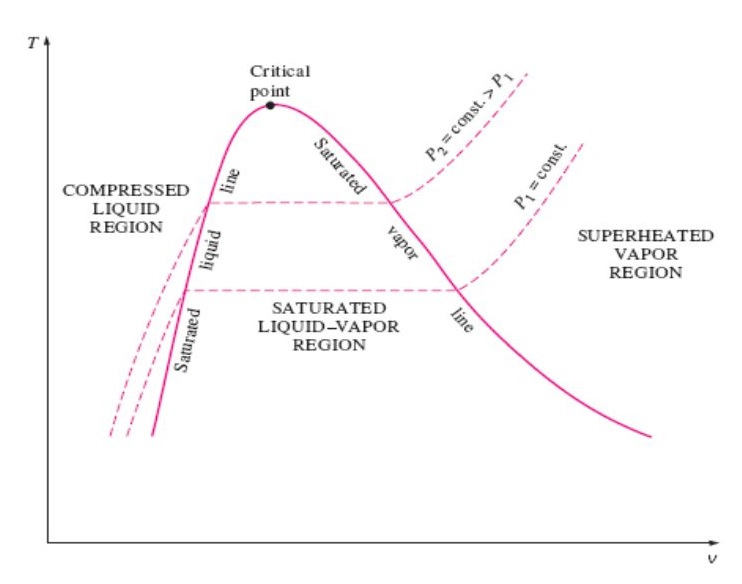
TV DIAGRAM OF PURE SUBSTANCE IN THERMODYNAMICS - Mechanical Engineering

thermodynamics - Can a liquid boil in a closed container? - Physics